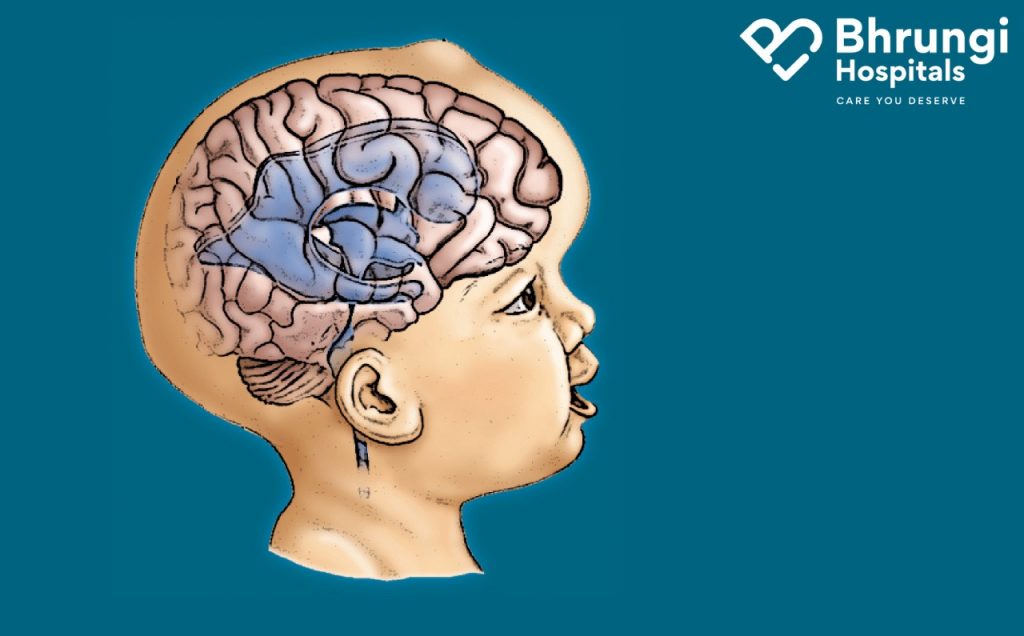
Hydrocephalus is the assemblage of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The extra fluid expands the ventricles and puts pressure on the brain.
Generally, cerebrospinal fluid flows through the ventricles and scours the brain and spinal column. However, the pressure of too much cerebrospinal fluid caused by hydrocephalus can damage brain tissues and render a variety of brain function issues.
Hydrocephalus can transpire at any age, but it is more common in infants and adults aged 60 and up. Hydrocephalus surgery can restore and maintain normal cerebrospinal fluid levels in the brain. Different therapies are frequently required to treat symptoms or problems caused by hydrocephalus.
Causes
An imbalance causes hydrocephalus in the cerebrospinal fluid produced and absorbed into the bloodstream.
Cerebrospinal fluid gets produced by brain tissues that line the ventricles. It moves through the ventricles via interconnected channels. The fluid finally finds its way into the brain and spinal column spaces. It is primarily absorbed by blood vessels in brain surface tissues.
| Distribution of cases | No. of Patients | Percentage |
| Congenital causes of hydrocephalus | ||
|
12
2 3 1 1 |
24
4 6 2 2 |
| Total | 19 | 38 |
| Acquired causes of hydrocephalus | ||
|
22
9 |
44
18 |
| Total | 31 | 62 |
| Total no. of case | 50 | 100 |
Distribution of cases according to etiology
| Symptom/Sign | No. of patients | Percentage (%) |
| Enlargement of head | 16 | 32 |
| Headache | 11 | 22 |
| Vomiting | 25 | 50 |
| Fever | 30 | 60 |
| Cough | 8 | 16 |
| Impaired conscious level | 10 | 20 |
| Convulsions | 22 | 44 |
| Incontinence | 2 | 4 |
| Dimness of vision | 4 | 8 |
| Difficulty in Walking | 4 | 8 |
| Excessive irritability | 12 | 24 |
| Involuntary movement | 1 | 2 |
| Significant past history | 7 | 14 |
| Significant family history | 2 | 4 |
Cerebrospinal fluid plays a vital role in brain function by:
- Maintaining brain buoyancy, allowing the relatively heavy brain to float within the skull.
- It is cushioned to protect the brain from injury.
- Getting rid of waste products from the brain’s metabolism.
- Flowing around and forth between the brain cavity and the spinal column to maintain a constant pressure within the brain and compensate for changes in blood pressure.
Risk factors
The cause of hydrocephalus is often unknown in many cases. However, various developmental or medical issues can contribute to or precipitate hydrocephalus.
Newborns
Hydrocephalus that is present at birth or shortly after birth can be caused by any of the following factors:
- A deficiency in the central nervous system can obstruct the flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- A possible complication of premature birth is bleeding within the ventricles.
- During pregnancy, infection in the uterus, such as rubella or syphilis, can cause inflammation in foetal brain tissues.
Other contributing factors
Other aspects that can contribute to hydrocephalus in people of any age include:
- Brain or spinal cord lesions or tumours
- Infections of the central nervous system, such as bacterial meningitis or mumps
- Bleeding in the brain as a result of a stroke or a head injury
- Other types of traumatic brain injury
Complications In most cases, hydrocephalus progresses, which means that if it is not treated, complications such as intellectual, developmental, and physical disabilities can occur. It is also potentially fatal. Less severe cases, if properly treated, may have few, if any, serious complications.
Some queries with answers
Is hydrocephalus curable?
There is no cure for hydrocephalus, but treatments allow those affected to live relatively everyday lives. In some cases, the blockage causing the fluid buildup in the brain can be surgically removed.
How is adult hydrocephalus treated?
The most typical treatment for hydrocephalus is a shunt, a flexible tube placed in the brain’s ventricular system and connected to a valve. A small hole in the skull is made, and the tube is gently guided through the brain to the fluid-filled ventricles.
What foods aid in the treatment of hydrocephalus?
The significance of a well-balanced diet
- Five servings of fruits and vegetables per day
- Carbohydrates derived from foods such as brown rice, potatoes, cereals, and whole wheat pasta
- Protein can be obtained from oily fish, eggs, and meat
Refer Below links for Quick consultation :
Evening Doctor Consultation Available