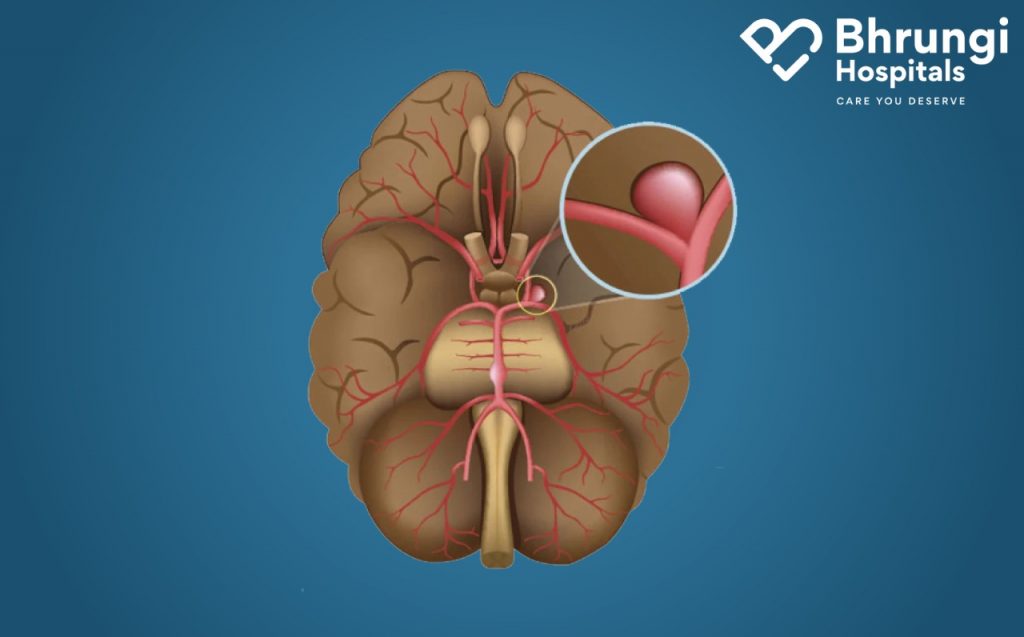
Brain aneurysm is a lump in a weak section of a blood vessel in or near your brain. The constant blood flow pushes the weakened section outward, forming a blister-like clot.
The aneurysm enlarges as blood rushes into the bulge. It’s similar to how a balloon thins and becomes more likely to pop as it fills with air. Brain bleeding occurs when an aneurysm leaks or ruptures (bursts open). It can sometimes cause a hemorrhagic stroke caused by bleeding in or around the brain and lead to brain damage and death.
Who gets brain aneurysms?
You are more likely to evolve a brain aneurysm if you:
- Are 40 to 60 years old.
- Are Female
- Have a family history of aneurysms
- Have a rare blood-vessel disorder like arterial dissection, fibromuscular dysplasia or cerebral arteritis.
- A genetic disorder affects connective tissue such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome, neurofibromatosis type 1 or Loeys-Dietz syndrome.
- Have polycystic kidney disease.
- They are born with a brain aneurysm as a birth defect.
| Annual incidence of Cerebral Aneurysms | Minimum | Maximum |
| Population | 6 | 16/100,000 |
| new cases | 76,500 | 204,100 |
Are aneurysms hereditary?
If one of your first-degree relatives has a cerebral aneurysm, you should have the rest of the family, children or siblings, checked out after consulting with your primary care physician. These examinations are typically performed with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan.
The link could be between 10% and 20%, according to studies. However, all studies have shown that relatives of aneurysm patients occasionally have an aneurysm. This risk increases if you or a family member has other risk factors for cerebral aneurysms.
What causes brain aneurysms?
It is unknown what causes a brain aneurysm to form. However, these factors, according to researchers, irritate and weaken blood vessels:
- Blood infection
- Smoking
- High blood pressure.
- Amphetamine and cocaine use.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Atherosclerosis.
What are the chances of enduring a brain aneurysm?
People can live their lives without being aware that they have an unruptured brain aneurysm. As long as it’s not broken, your chances are good. However, there is a risk that the brain aneurysm will rupture, which is determined by various factors such as aneurysm size, location, and others; if an aneurysm ruptures, blood leaks into the space surrounding your brain and, in some cases, into the brain tissue itself, resulting in a hemorrhagic stroke.
A ruptured brain aneurysm necessitates immediate medical attention. The likelihood of death or disability increases as time passes with a ruptured aneurysm. Approximately 75% of people with a ruptured brain aneurysm survive for more than 24 hours. However, one-quarter of the survivors may face life-threatening complications within six months.
Summary
A sudden, severe headache may indicate a brain aneurysm with or without stroke symptoms. A ruptured brain aneurysm is a serious, potentially fatal condition requiring immediate medical attention and emergency treatment. If you have an unruptured brain aneurysm, discuss the risks and benefits of various treatment and management options with your healthcare provider.
Answers to some questions
Are there any symptoms of an aneurysm?
An aneurysm occurs when pressure causes a weak point in a blood vessel to balloon, resulting in a small sac or bulge formation. Severe headaches, nausea, vomiting, double vision, seizures, cardiac arrest, and loss of consciousness are all warning signs.
Is it possible for a 12-year-old to have a brain aneurysm?
Aneurysms in the brain are sporadic in children and may not cause any symptoms until they burst or rupture. Ruptured brain aneurysms can be fatal, and the child will require immediate treatment to minimize brain damage.
Aneurysms are painful?
An aneurysm is a bulging, weakened section of an artery wall that can occur anywhere in the body. The most familiar sign is a pain in the aneurysm’s location.
Refere Below Links :