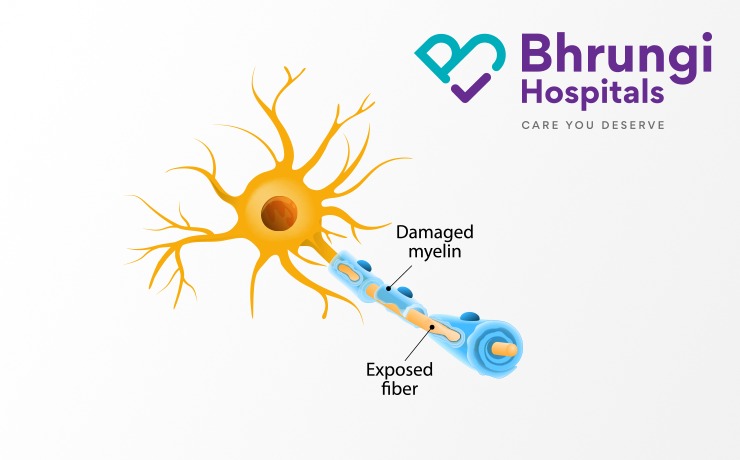
The central nervous system includes the brain and spine. The nerves of the arm are similar to a telephone wire. The peripheral nervous system is made up of these nerves. Information about the environment and the position of our pen is carried on sensory nerves. Motor nerves carry bioelectrical information to muscles. The neuromuscular junction is where the nerve and muscle meet. There is a disorder that prevents nerves from functioning properly. It can cause paralysis if a nerve is completely lacerated. Depending on the type and severity of the neuropathy, the disease causes varying degrees of weakness. Damage to the peripheral nerves that transmit pain and temperature sensations can prevent people from knowing that they have been injured or that a wound is getting worse. Recently in various studies, the prevalence of peripheral nerve disorder varied from 5 to 2400 per 10,000 population.
What is Peripheral Nerve Disorder?
The network of nerves that send information from your brain to the rest of your body is called the central nervous system. Damage to the nervous system is called peripheral neuropathy or peripheral nerve disorder. Basically, It is a problem with the peripheral nervous system.
Symptoms Peripheral Nerve Disorder
Depending on the type of peripheral neuropathy you have, the symptoms can be different. Symptoms can range from mild to more serious effects such as burning pain or paralysis. Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include:
- Muscle weakness
- Cramps
- Muscle twitching
- Loss of muscle and bone Changes in skin, hair, or nails Numbness
- Loss of sensation or feeling in body parts
- Loss of balance or other functions as a side effect of the loss of feeling in the legs, arms, or other body parts Emotional disturbances
- Sleep disruptions
- Loss of pain or sensation that can put you at risk, such as not feeling an impending heart attack or limb pain Inability to sweat properly, leading to heat intolerance
- Loss of bladder control, leading to infection or incontinence
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting because of a loss of control over blood pressure
- Diarrhea, constipation, or incontinence related to nerve damage in the intestines or digestive tract
- Trouble eating or swallowing
- Life-threatening symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or irregular heartbeat
- The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy may be similar to other conditions. You should always see a healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy may be similar to other conditions. You should always see a healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Peripheral Neuropathy Causes
There are many different causes of peripheral neuropathy. Some people have the disorder from their parents. Some people develop it because of an injury or another disorder, while others develop it because of a different problem like hormone imbalance or a kidney condition
Peripheral Neuropathy Types
There are more than 100 different types of peripheral neuropathy. They are broken down into the following categories to help doctors classify them.
- Motor neuropathy
The nerves that control movement in the body are damaged.
- Sensory neuropathy
Pain, temperature, and a light touch are all controlled by sensory nerves. These groups of nerves are affected by sensory neuropathy.
- Autonomic nerve neuropathy
Breathing and heartbeat are controlled bionomic nerves, which are not conscious of it. These nerves can be damaged.
- Combination neuropathies
You may have more than one type of neuropathies, such as a sensory-motor neuropathy.
Peripheral Neuropathy Diagnosis
It may be difficult to make a diagnosis of the symptoms and body parts affected by peripheral neuropathy.
If your healthcare provider suspects nerve damage, he or she will take an extensive medical history and do a number of
neurological tests to determine the location and extent of the damage. These could include:
- Blood tests
- Spinal fluid tests
- Muscle strength tests
- Tests of the ability to detect vibrations
Depending on what basic tests reveal, your healthcare provider may want to do more in-depth scanning and other tests to get a better look at your nerve damage. Some tests may include:
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies
- Nerve and skin biopsy
Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment
A lot of things can be done to prevent peripheral neuropathy from getting worse. If an underlying condition like diabetes is to blame, your healthcare provider will treat the pain and other symptoms first.
Over-the-counter painkillers can help in some cases. There are times when prescription medicines are needed. Antileisure drugs, such as phenytoin, and carbamazepine, as well as some classes of antidepressants, include mexiletine, a medicine developed to correct irregular heart rhythms. Other instances of pain may be helped by lidocaine injections and patches. In extreme cases, surgery can be used to destroy nerves or repair injuries that are causing pain.
Peripheral Neuropathy Prevention
It is possible to prevent peripheral neuropathy by making lifestyle choices. You can reduce your risk by avoiding alcohol, eating a healthy diet, avoiding toxins, and exercising regularly. If you have chronic health conditions such as diabetes, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to control your condition, which may prevent or delay the start of peripheral neuropathy.
Peripheral Neuropathy Management
Even if you already have some form of peripheral neuropathy, healthy lifestyle steps can help you feel better and reduce the pain. You’ll also want to quit smoking, not let injuries go untreated, and be meticulous about caring for your feet and treating wounds to avoid complications, such as the loss of a limb. Hand and foot braces can help you to make up for weakness in your muscles. It’s possible to walk better with the help of orthotics. Yoga can help ease emotional stress and physical symptoms.