According to International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), in India every year around 13 lakh women are detected to have Cervical cancer, and out of which more than 77,000 succumb to the disease. Shockingly, Cervical cancer ranks as the 2nd most frequent cancer among women in our country with an Age-standardised mortality rate of 11.4 %. This means out of every 1 lakh women in various age groups from 15-44, 11.4 % die from cervical cancer.
| Incidence | Mortality | |
| Annual number of new cases/deaths | 123907 | 77348 |
| Crude rate | 18.7 | 11.7 |
| Age-standardized rate | 18.0 | 11.4 |
| Cumulative risk 0-74 years (%) | 2.01 | 1.30 |
| Ranking of cervical cancer (all years) | 2nd | 2nd |
Does this mean Cervical cancer is a deadly disease? The answer is NO. Having awareness on it, Early detection and vaccine could save our women from this cancer. So, in this article, we will be addressing these three sections that would help you or women around you to understand major aspects of cervical cancer.
What is Cervical Cancer?
Our body is made up of trillions of cells. Normally, as we grow older, some cells will die and at the same time, new cells will be created. But, when this natural process goes out of control, that means cells keep making new cells and the old or abnormal ones don’t die, they will form as tumours. This is what we generally call Cancer. When this particular condition is developed in a woman’s cervix, it is called Cervical cancer.
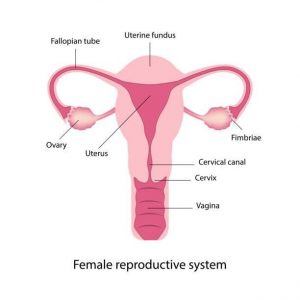
What is Cervix?
Cervix is part of the female reproductive system and is located in the lower part of the womb (Uterus), forming the opening from the womb to the vagina. It plays an important role in a woman’s reproductive system by keeping unhealthy things out of your body, like bathwater and helps in keeping the baby in place until it’s fully developed when they are pregnant.
What Causes Cervical Cancer?
Nearly, 99 % of Cervical cancer cases are attributed to a virus called Human Papilloma Virus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection.
Other factors that can also increase your risk include:
- human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- Smoking
- Obesity
- a family history of cervical cancer
- Taking Birth control pills
- having three full-term pregnancies
- being younger than 17 when you got pregnant for the first time
Now, we will discuss the major cause of cervical cancer, i.e., HPV.
Human Papilloma Virus:
It is a group of viruses that are quite common worldwide and one of the causative agents in the sexually transmitted infections in men and women with and without clinical lesions. There are more than 100 types of HPV, of which at least 14 are cancer-causing (also known as high-risk types). Among these 14 high risk types, two variants, HPV-16 and HPV- 18 are the reason for 70% of cases.
Based on ICO HPV Information Centre research, about 83.2% of invasive cervical cancers showed the presence of HPVs 16 or 18.
When a person is infected with HPV, his/her immune system usually prevents the virus from doing serious harm. But sometimes, either due to immune system failure or other reasons the virus survives for years.
Eventually, the virus can lead to the conversion of normal cells on the surface of the cervix into cancerous cells, i.e., Cervical Cancer
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer:
Major symptoms include
- Irregular or Post-Menopausal Bleeding
- Increased Vaginal Discharge
In addition to these, the following could be the symptoms
- Bleeding after sexual
- Discomfort during sexual
- Pelvic pain
Any of the above symptoms doesn’t mean you have Cervical cancer. But you should consult your doctor as a precautionary measure.
How a woman can be protected from Cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is successfully treatable if it is detected and diagnosed early. This early detection of cancer cells is popularly known as Screening and Cervical cancer screening is an essential part of a woman’s routine health care. To detect Cervical cancer, a method of cervical screening to test the presence of precancerous or cancerous cells on the cervix is used and it is called as Pap Smear Test or Pap test.
Detecting these abnormal cells on the cervix early with a Pap smear is the first step in halting the possible development of cervical cancer.
Pap smear Test:
This test is performed in a hospital clinic where the woman lies on an examination table. A health care professional inserts an instrument called a speculum into her genitals so that the upper portion of the vagina and the cervix can be examined.
This procedure also allows the health care professional to take a sample of cervical cells using a small brush to gently remove cells from the surface of the cervix and the area around it so they can be checked in a laboratory under a microscope for cervical cancer or cell changes that may lead to cervical cancer. After your Pap smear, patient can go about her day without restrictions.
To know more about Pap smear test, consult our Gynaecologist….
| HPV 16/18 prevalence: | No. Tested | % (95% CI) |
| Normal cytology | 8845 | 5.0 (4.6-5.5) |
| Low-grade cervical lesions | 177 | 28.2 (22.1-35.3) |
| High-grade cervical lesions | 253 | 62.8 (56.7-68.6) |
| Cervical cancer | 2006 | 83.2 (81.5-84.8) |
As per WHO, to end cervical cancer 7 out of 10 women should be screened by 35 years old. It is advisable for women aged above 21 should be screened with a Pap test every 3 years
HPV Vaccination:
Virologist Harald zur Hausen discovered how cervical cancer is triggered by virus infections. His work led to the creation of the HPV vaccine which cuts the risk of developing cervical cancer. As per WHO guidelines, to end cervical cancer, 9 out 0f 10 girls should be vaccinated against HPV.
The Indian Academy of Paediatrics Committee on Immunization (IAPCOI) recommends that HPV vaccines be given in two doses, six months apart for girls below the age of 14 years. For those who are 15 and older, the vaccine is given in a three-dose regimen.